The occurrence of post-stroke depression results from the effects of biological, psychological, and social factors, likely involving neurotransmitters, neuroendocrine effects, nerve anatomy, neurotrophic factors, neural regeneration, inflammatory reactions, and social psyche factors. Synaptotagmin promotes neurotransmitter release, regulates the transfer of synaptic vesicle to synaptic active zones, and is a key factor in information transfer among neurons. The Xingnao Jieyu capsule has been shown to effectively relieve neurologic impairments and lessen depression. It remains poorly understood whether this capsule can be used to treat post-stroke depression. Thus, Prof. Yongmei Yan and team from Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine found that the Xingnao Jieyu capsules upregulated synaptotagmin expression in the hippocampi of rats with post-stroke depression, and improved depression symptoms. The therapeutic effects of Xingnao Jieyu capsules were similar to those of fluoxetine. These results, published in the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 8, No. 19, 2013), can provide scientific evidence and theoretical basis for pathogenesis and treatment of post-stroke depression.
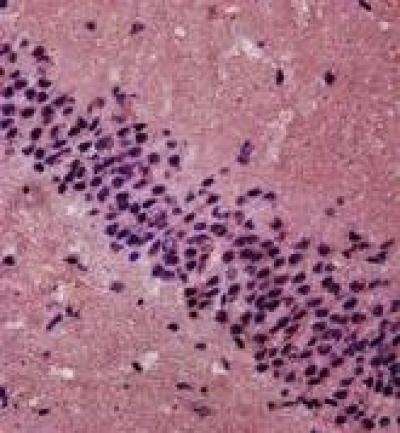
0.41 g/kg Xingnao Jieyu capsule medicine powder was dissolved in 2 mL distilled water for intragastric administration and found that the number of synaptotagmin-positive cells (arrows) was significantly higher in the hippocampal CA1 region of rats with post-stroke depression.
(Photo Credit: Neural Regeneration Research)
Source: Neural Regeneration Research