Tropical Cyclone Hellen made landfall in west central Madagascar as NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead capturing temperature data on its towering thunderstorms.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Madagascar on March 31 at 10:47 UTC/6:47 a.m. EDT and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard captured infrared data on Hellen. AIRS data showed powerful thunderstorms circling the center of circulation with cloud top temperatures in excess of -63F/-52C indicating they were high into the troposphere. Thunderstorms reaching those heights also have the potential for heavy rainfall
Hellen developed during the week of March 23 in the Mozambique Channel, the body of water that lies between the island nation of Madagascar and Mozambique on the African mainland. By March 26, at 20:00 UTC/4 p.m. EDT, the tropical low, then known as System 95S was centered near 10.7 south latitude and 39.4 east longitude. The low level center was actually over land just inland from the coast, and sitting over the Tanzania and Mozambique border.
It was on March 26, that the Joint Typhoon Warning Center or JTWC noted that the low had a high chance for becoming a tropical depression in the next 24 hours. JTWC noted that enhanced infrared satellite imagery on March 26 revealed that the low-level circulation center has consolidated and there were bands of thunderstorms wrapping into it. JTWC estimated that maximum sustained winds are between 25 to 30 knots/ 28.7 to 34.5 mph/46.3 to 55.5 kph.
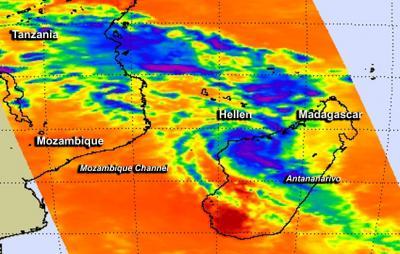
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Madagascar on Mar. 31 at 10:47 UTC/6:47 a.m. EDT, it showed powerful thunderstorms circling the center of Hellen (purple).
(Photo Credit: NASA/JPL, Ed Olsen)
At that time, the tropical low was in an area that had low vertical wind shear and warm sea surface temperatures that forecasters at JTWC said would provide the fuel for thunderstorms to develop and assist the low's growth. Over the next several days, System 95S moved east and back into the Mozambique Channel where it rapidly intensified into Tropical Cyclone Hellen and reached Category IV status on the Saffir-Simpson Scale when maximum sustained winds peaked near 140 knots/161.1 mph/259.3 kph.
By March 31 at 1500 UTC/11 a.m. EDT, Hellen's maximum sustained winds dropped to 85 knots/97.8 mph/ 157.4 kph because of the interaction with Madagascar. It was centered near 16.2 south latitude and 45.9 east longitude, about 180 nautical miles/207.1 miles/333.4 km north-northwest of Antananarivo, Madagascar.
The NOAA-19 satellite showed that the bulk of strongest thunderstorms were south of the center as a result of wind shear. In addition there is dry air moving into the center of circulation which is also helping to weaken Hellen.
Hellen was moving slowly to the south-southeast at 5 knots/5.7 mph/9.2 kph, and the JWTC expects it to curve to the southwest and re-enter the Mozambique Channel.
Source: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center