Porphyrins are organic molecules that appear in the central region ofmacromolecules such as chlorophyll and hemoglobin, and have a metal atomat their center that determines their specific function. The importance of these moleculesin the field of molecular electronics lies in their "ease of transferelectrons from one region to another" explains the responsible of the work at the Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology Research Center (a joint research center of the CSIC, the University of Oviedo and the Government of the Principality of Asturias) Víctor Manuel García.
To determine the electronic transport mechanism in porphyrins, theteam has evaluated the change in their electrical conductivity as a function ofdistance and temperature, in chains of one, two and three units of porphyrinanchored at their ends to gold surfaces, which act as electrodes.
According to the laws governing hopping transport, the conductivity of the porphyrins increases with temperature but decreases slowly with distance. Under thismechanism, electrons pass from one electrode to another by jumping from one regionof the molecule to another, thus being their movement moresimilar to that of a particle than to a wave. The temperature increases their ability to jump and, therefore, the conductance, while the length decreases it.
On the contrary, the tunneling effect is based on the fact that electrons have a certain probability of disappearing from one electrode and reappearing in the other. This probability depends on the type of molecule between the electrodes.
Under this mechanism, the temperature can also increase the electrical conductance, "since it increases the amount of available electrons to be transported", explains García. However, the length effect changes the conductance exponentially. A increase of the length of the molecular wire drastically decreases the probability of electrons to appear at the other side.
The weak dependence of the porphyrins' conductivity as a function of distance as well as the temperature dependence "led to believe that the main transport mechanism washopping. However, experiments and theoretical calculations carried out by theresearch team have shown that electron transport in these systems is actually led by the tunneling effect", says the researcher.
Computer Components
"The progressive miniaturization of integrated circuits make the electronic elementsincreasingly approach the atomic limit", says Garcia. Therefore,the research aims to find molecules that can perform the functions ofelectronic components since they can be produced in a simple and cost-effective way.The electron transport mechanism shown in this study may promotethe use of porphyrins in devices for quantum computers. These computers arebased on quantum mechanics, so the transport of electrons by tunnelingmay be appropriate for them. When electrons disappear and reappear at one electrode or another "they retain their wave nature, and therefore also theirquantum properties", concludes Garcia.
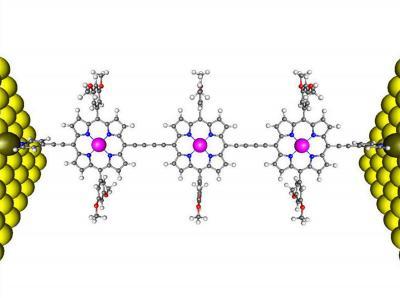
Gold surfaces joint by three units of porphyrin.
(Photo Credit: Centro de Investigación en Nanomateriales y Nanotecnología)
Source: CSIC, Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas