In 1980 and 1981 NASA's Voyager 1 and 2 space probes passed for the first time over the planet Saturn, located 1,500 million km from the Sun. Among their numerous discoveries they observed a strange, hexagon-shaped structure in the planet's uppermost clouds surrounding its north pole. The hexagon remained virtually static, without moving, vis-à-vis the planet's overall rotation that was not accurately known. What is more, the images captured by the Voyager probes found that the clouds were moving rapidly inside the hexagon in an enclosed jet stream and were being dragged by winds travelling at over 400 km/h.
Thirty years later –the equivalent of one Saturn year, in other words, the time the planet takes to go all the way around the Sun– and over more than six consecutive years, researchers in the UPV/EHU's Planetary Sciences Group, in collaboration with astronomers from various countries, were able to observe Saturn's northern polar region in detail once again and confirmed that the hexagon continued in place. After measuring the positions of the hexagon vertices with great precision, they determined that its movement remains extremely stable, and on the basis of the cloud movements, that the jet stream inside it remains unchanged. For this study the researchers used images taken from the Earth between 2008 and 2014; they used, among others, the astronomical cameras PlanetCam (developed by the Planetary Sciences Group itself) and Astralux, fitted to the telescopes of the Calar Alto Observatory in Almería (Spain); in addition, they used the very high resolution images obtained by the Cassini spacecraft, which has been orbiting Saturn since 2004.
Due to the tilt of approximately 27º of the planet Saturn, its polar atmosphere undergoes intense seasonable variations with long polar nights lasting over seven years, followed by a long period of 23 years of variable illumination. However, the seasonal variations do not affect the hexagon and its jet stream at all, so both are part of an extensive wave, deeply rooted in Saturn's atmosphere. The UPV/EHU researchers suggest that the hexagon and its stream are the manifestation of a "Rossby wave" similar to those that form in the mid-latitudes of the earth. On our planet the jet stream meanders from west to east and brings, associated with it, the system of areas of low pressure and anticyclones which we have been seeing regularly on weather maps.
On Saturn, a hydrogen gas planet, ten times the size of the Earth, cold in its upper clouds, without a solid surface, and with an atmosphere as deep as that of an ocean, "the hexagonal wavy motion of the jet stream is expected to be propagated vertically and reveal to us aspects of the planet's hidden atmosphere," pointed out Agustín Sánchez-Lavega, Head of the Planetary Sciences research group. "The movement of the hexagon could therefore be linked to the depths of Saturn, and the rotation period of this structure, which, as we have been able to ascertain, is 10 hours, 39 minutes and 23 seconds, could be that of the planet itself," he added. Saturn is the only planet in the Solar System whose rotation period is not yet known.
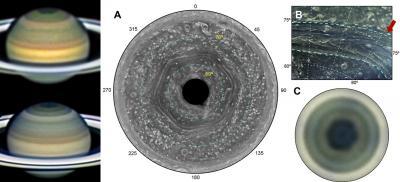
On the left, Saturn is shown in images obtained in 2013 with the PlanetCam and Astralux cameras on the 1.23 m and 2.2 m telescopes at the Calar Alto Observatory. The hexagon forms the edge of the dark region on the planet's north pole. On the right, maps are shown of the north pole of Saturn depicting the hexagonal structure: (A) Cassini ISS (Jan. 3, 2009); (B) Detail of the clouds inside the hexagon (Cassini ISS on Aug. 26, 2008); (C) 2.2 m telescope of the Calar Alto Obervatory: Astralux camera (Jul. 13-16, 2013).
(Photo Credit: Left image: Planetary Science Group Universidad del País Vasco/Euskal Herriko UnibertsitateaRight image: Planetary Science Group Universidad del País Vasco/Euskal Herriko Unibertsitatea-Cassini NASA/European Space Agency)
Source: Universidad del País Vasco