Scientists have demonstrated how noise in a microwave amplifier is limited by self-heating at very low temperatures.
Many significant discoveries in physics and astronomy are dependent upon registering a barely detectable electrical signal in the microwave regime. A famous example of this was the discovery of cosmic background radiation that helped confirm the Big Bang theory. Another example is the detection of data from scientific instruments in space missions on their way to distant planets, asteroids or comets.
Faint microwave signals are detected by transistor-based low-noise amplifiers. Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology have now optimised indium phosphide transistors using a special process for this purpose. A spin-off company from Chalmers, Low Noise Factory, designs and packages amplifier circuits.
"Cooling the amplifier modules to -260 degrees Celsius enables them to operate with the highest signal-to-noise ratio possible today," says Jan Grahn, Professor of microwave technology at Chalmers. "These advanced cryogenic amplifiers are of tremendous significance for signal detection in many areas of science, ranging from quantum computers to radio astronomy."
Using a combination of measurements and simulations, the researchers investigated what happens when a microwave transistor is cooled to one tenth of a degree above absolute zero (-273 degrees Celsius). It was thought that noise in the transistor was limited by so-called hot electrons at such extreme temperatures. However, the new study shows that the noise is actually limited by self-heating in the transistor.
Self-heating is associated with phonon radiation in the transistor at very low temperatures. Phonons are quantum particles that describe the thermal conductivity of a material. The results of the study are based on experimental noise measurements and simulations of phonons and electrons in the semiconductor transistor at low temperatures.
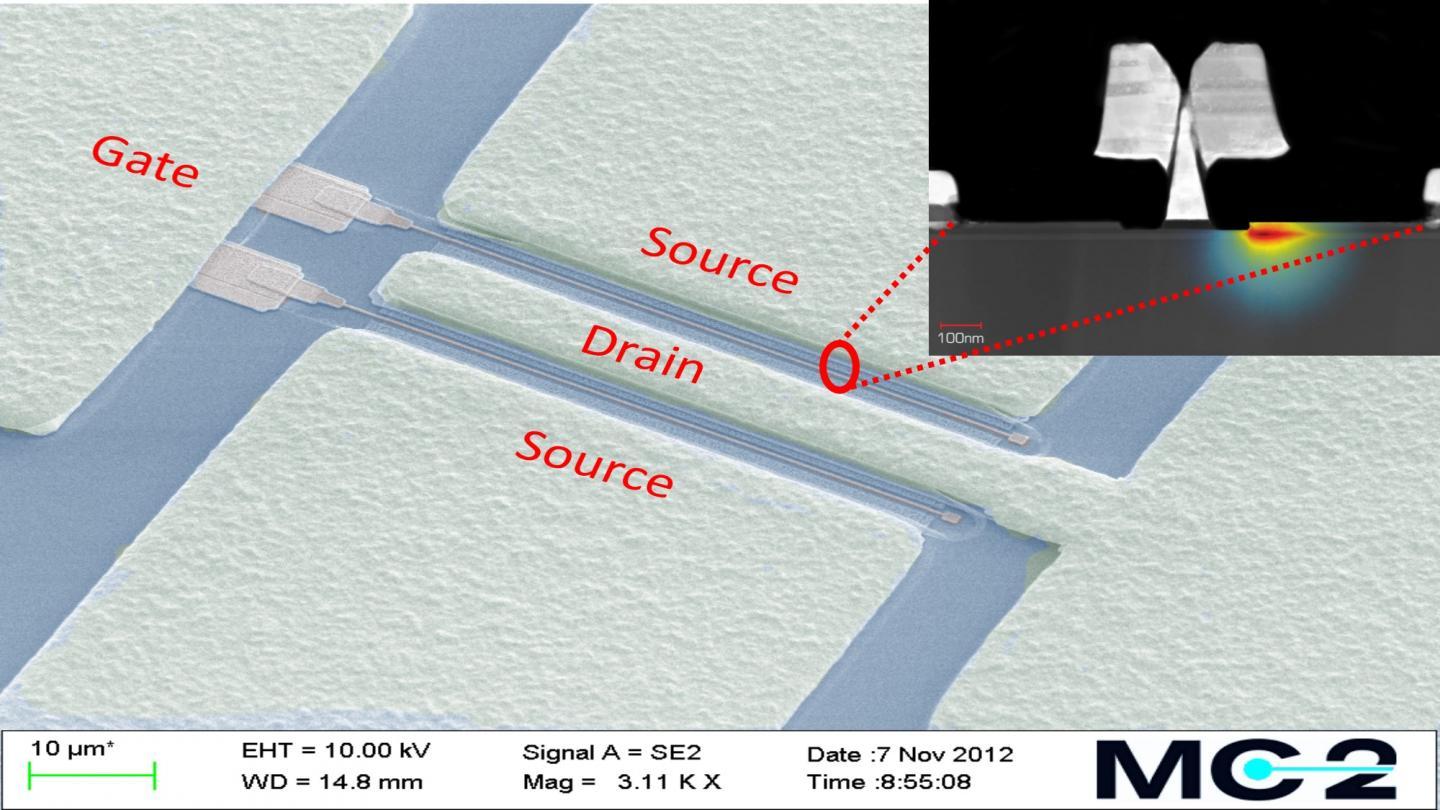
This is an electron microscope image of an indium phosphide high electron mobility transistor (InP HEMT). The region affected by the self-heating process is highlighted in the cross section of the InP HEMT.
(Photo Credit: Chalmers University of Technology)
"The study is important for the fundamental understanding of how a transistor operates close to absolute zero temperature, and also how we should design even more sensitive low-noise amplifiers for future detectors in physics and astronomy," explains Jan Grahn.
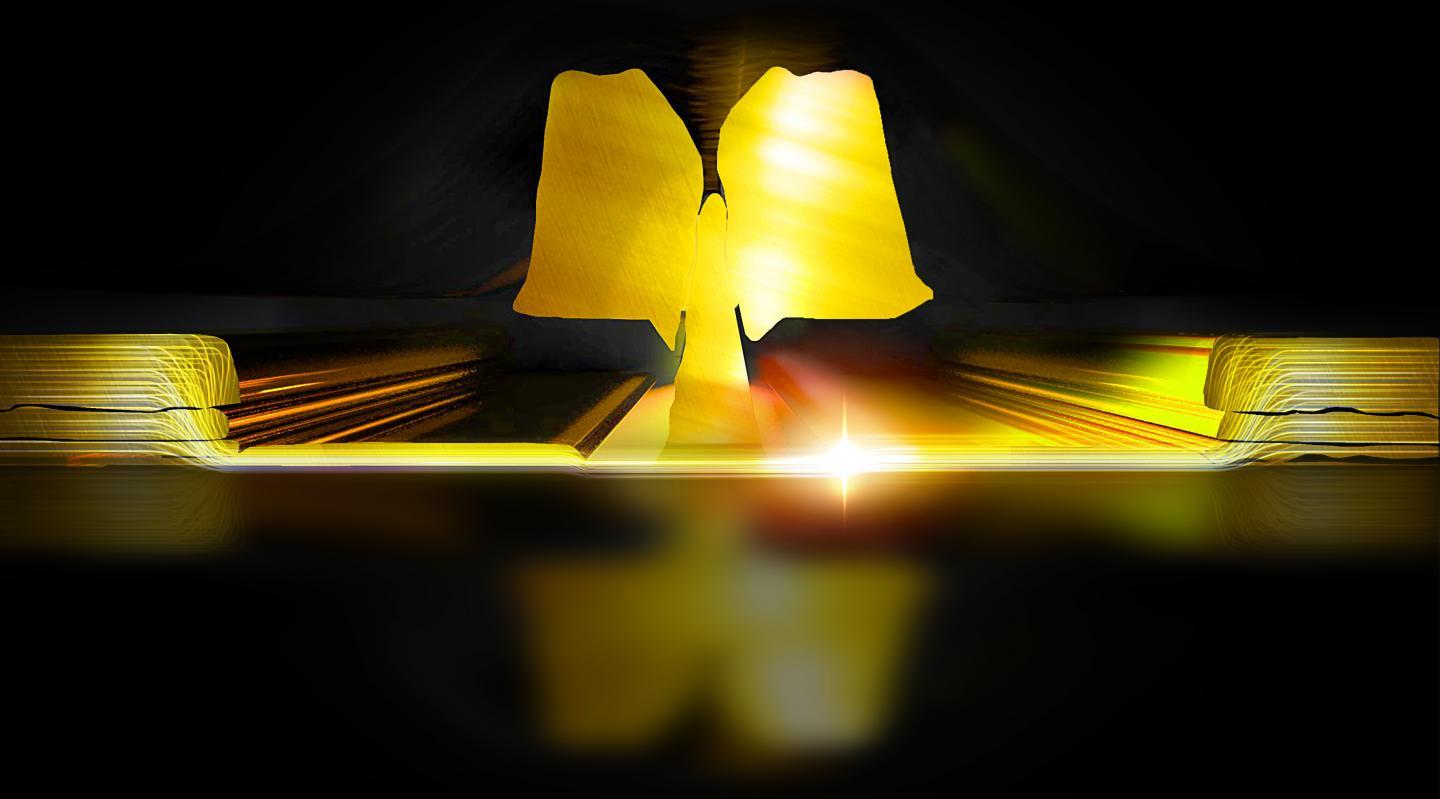

This is a cross sectional image of an ultra-low noise transistor. Electrons, accelerated in the high mobility channel under the 100 nanometer gate, collide and dissipate heat that fundamentally limits the noise performance of the transistor.
(Photo Credit: Lisa Kinnerud and Moa Carlsson, Krantz NanoArt)
The results will be published in Nature Materials.