Once the desired shape has been framed by a length of single-stranded DNA, short DNA "staple strands" integrate the structure and act as the glue to hold the desired shape together. The nucleotide sequence of the scaffold strand is composed in such a way that it runs through every helix in the design, like a serpentine thread knitting together a patchwork of fabric. Further reinforcement is provided by the staple strands, which are also pre-designed to attach to desired regions of the finished structure, through base pairing.
"To make curved objects requires moving beyond the approximation of curvature by rectangular pixels. People in the field are interested in this problem. For example, William Shih's group at Harvard Medical School recently used targeted insertion and deletion of base pairs in selected segments within a 3D building block to induce the desired curvature. Nevertheless, it remains a daunting task to engineer subtle curvatures on a 3D surface, " stated Yan.
"Our goal is to develop design principles that will allow researchers to model arbitrary 3D shapes with control over the degree of surface curvature. In an escape from a rigid lattice model, our versatile strategy begins by defining the desired surface features of a target object with the scaffold, followed by manipulation of DNA conformation and shaping of crossover networks to achieve the design," Liu said.
To achive this idea, Yan's graduate student Dongran Han began by making simple 2-dimensional concentric ring structures, each ring formed from a DNA double helix. The concentric rings are bound together by means of strategically placed crossover points. These are regions where one of the strands in a given double helix switches to an adjacent ring, bridging the gap between concentric helices. Such crossovers help maintain the structure of concentric rings, preventing the DNA from extending.
Varying the number of nucleotides between crossover points and the placement of crossovers allows the designer to combine sharp and rounded elements in a single 2D form, as may be seen in figure 1 a & b, (with accompanying images produced by atomic force microscopy, revealing the actual structures that formed through self-assembly). A variety of such 2D designs, including an opened 9-layer ring and a three-pointed star, were produced.
The network of crossover points can also be designed in such a way as to produce combinations of in-plane and out-of-plane curvature, allowing for the design of curved 3D nanostructures. While this method shows considerable versatility, the range of curvature is still limited for standard B form DNA, which will not tolerate large deviations from its preferred configuration—10.5 base pairs/turn. However, as Jeanette Nangreave, one of the paper's co-authors explains, "Hao recognized that if you could slightly over twist or under twist these helices, you could produce different bending angles."
Combining the method of concentric helices with such non-B-form DNA (with 9-12 base pairs/turn), enabled the group to produce sophisticated forms, including spheres, hemispheres, ellipsoid shells and finally—as a tour de force of nanodesign—a round-bottomed nanoflask, which appears unmistakably in a series of startling transmission electron microscopy images (see figure 1, c-f )
"This is a good example of teamwork in which each member brings their unique skills to the project to make things happen." The other authors include Suchetan Pal and Zhengtao Deng, who also made significant contributions in imaging the structures.
Yan hopes to further expand the range of nanoforms possible through the new technique. Eventually, this will require longer lengths of single-stranded DNA able to provide necessary scaffolding for larger, more elaborate structures. He credits his brilliant student (and the paper's first author) Dongran Han with a remarkable ability to conceptualize 2- and 3D nanoforms and to navigate the often-perplexing details of their design. Ultimately however, more sophisticated nanoarchitectures will require computer-aided design programs—an area the team is actively pursuing.
The successful construction of closed, 3D nanoforms like the sphere has opened the door to many exciting possibilities for the technology, particularly in the biomedical realm. Nanospheres could be introduced into living cells for example, releasing their contents under the influence of endonucleases or other digestive components. Another strategy might use such spheres as nanoreactors—sites where chemicals or functional groups could be brought together to accelerate reactions or carry out other chemical manipulations.

This animation reflects the contour of a sphere made of rings of DNA double helices connected together (staple strand crossovers are not shown here), using the Yan groups new technique of DNA origami. Additional structures assembled through this method are also displayed.
(Photo Credit: The Biodesign InstituteArizona State University)
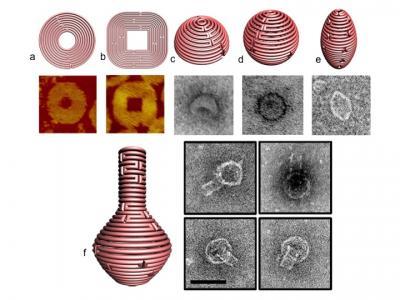
Figure 1 a and b display schematics for 2-D nanoforms with accompanying AFM images of the resulting structures. 1 c-e represent 3D structures of hemisphere, sphere and ellipsoid, respectively, while figure 1f shows a nanoflask, (each of the structures visualized with TEM imaging).
(Photo Credit: The Biodesign Institute Arizona State University)
Source: Arizona State University