Tropical Cyclone Ian has been battered by wind shear and infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite revealed that the bulk of the precipitation has been pushed east and southeast of the storm's center.
On January 13 at 0900 UTC/4 a.m. EST, Tropical Cyclone Ian's maximum sustained winds were near 65 knots/74.8 mph/120.4 kph, just at hurricane-strength. Just a day before, Ian's maximum sustained winds were near 80 knots/148.2 kph/92.0 mph. Ian is moving to the southeast at 14 knots/25.9 kph/16.1 mph and is expected to continue in that direction. Ian was located about 882 nautical miles/1,633 km/1,015 miles south of Pago Pago, near 29.5 south and 169.9 west.
Ian has become significantly elongated as it has been battling strong wind shear. The precipitation has also been sheared to the east.
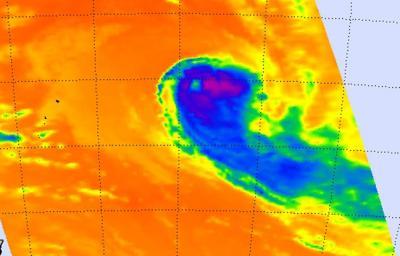
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Ian on Jan. 13 at 01:23 UTC and saw strongest storms with the coldest cloud tops had temperatures (purple) east and southeast of the center.
(Photo Credit: NASA JPL, AIRS)
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Ian on January 13 at 01:23 UTC/January 12 at 8:23 p.m. EST, the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument captured an infrared picture of the storm. Infrared data showed the temperature of the storm's clouds and the sea surface temperatures surrounding it. The strongest storms with the coldest cloud tops had temperatures as cold as -63F/-52C and the AIRS image showed those storms were clearly pushed east and southeast of the center. The AIRS data also showed warmer, lower cloud top temperatures north and west of Ian's center.
AIRS data showed sea surface temperatures north of Ian were as warm as 300K/26.5C/80.3F/ while those south of Ian (and in the general direction the storm was heading) were near 290K/16.8C/62.3F or cooler.
Over the next couple of days, Ian is expected to become extra-tropical and a cold core low pressure area in the next day and a half.
Ian is no threat to land as it continues on its southeastern track.
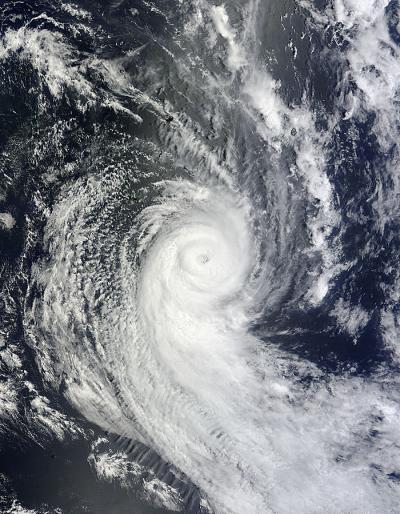

NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Cyclone Ian on Jan. 11 at 2200 UTC and the MODIS instrument captured this visible image of the storm.
(Photo Credit: NASA Goddard MODIS Rapid Response Team)
Source: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center