As Tropical Cyclone Madi began its landfall in southeastern Tamil Nadu, India NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead and captured an image of the weakening storm. Several factors are responsible for Madi's quick weakening.
The MODIS or Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer instrument aboard Aqua captured a visible image of Madi on Dec. 12 at 05:05 UTC/12:05 a.m. EST that showed the strongest thunderstorms were wrapped around the center of circulation. This strongest thunderstorms have weakened since Aqua passed overhead and Madi was devoid of any strong convection by 1500 UTC/10 a.m. EST. There was also a band of thunderstorms wrapping into the northern quadrant from the east. The southern extent of the tropical cyclone's clouds were over extreme northern Sri Lanka.
Madi continued to weaken from a combination of dry air moving into the system, increased wind shear and interaction with land.
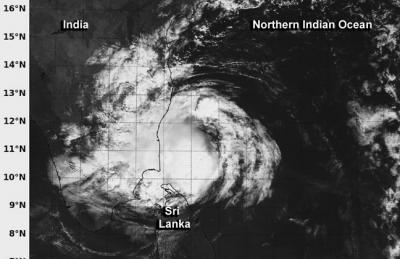
NASA's Aqua satellite captured this visible image of Tropical Cyclone Madi as it began making landfall along the southeastern coast of India on Dec. 12 at 05:05 UTC/12:05 a.m. EST.
(Photo Credit: : NRL/NASA)
The final advisory on the tropical cyclone was issued by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center on December 12 at 0300 UTC/December 11 at 10 p.m. EST. At that time, Madi's maximum sustained winds had decreased to 35 knots/40.2 mph/64.8 kph and were weakening. At that time, Madi's center was about 115 nautical miles/ 132.3 miles/213 km east-southeast of Chennai, India, near 12.2 north and 82.0 east. It was moving to the southwest at 10 knots/11.5 mph/18.5 kph.
Madi's remnants are expected to continue on a southwestern track over extreme southern India and dissipate over land.
Source: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center