Powerful hurricane Raymond, located off Mexico's south-central Pacific coast, weakened to a tropical storm and has dropped a lot of rain over central western Mexico's coast. NASA's TRMM satellite measured rainfall from space and that data was used to create a rainfall total map.
Raymond has now started to move slowly away from the location where it has been parked since Monday October 21, 2013. Raymond dropped abundant rainfall in much of the same area already hit by deadly flooding and landslides with Hurricane Manuel in September.
The rainfall analysis above was made at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. using Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite or TRMM-based, near-real time Multi-satellite Precipitation data (TMPA) collected during the period from October 15 to 23, 2013. Rainfall totals greater than 125mm/~4.9 inches occurred in the coastal area northeast of Raymond. The analysis also indicates that rainfall totals were greater than 350mm/ ~13.8 inches along the coast northwest of Acapulco. During the past week extreme rainfall amounts of over 560mm/~22 inches fell in the open waters of the Pacific where Raymond was stalled.
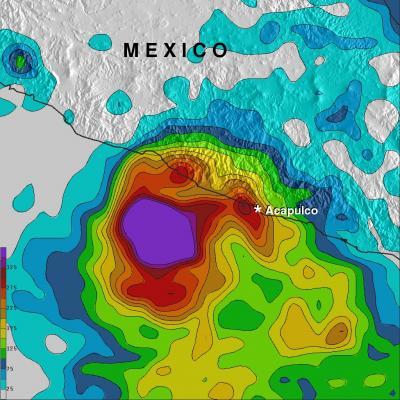
TRMM rainfall map from Oct. 15-23 shows rainfall totals greater than 125mm/~4.9 inches (red) northeast of Raymond's center. More than 350mm/ ~13.8 inches (red) fell along the coast northwest of Acapulco. Over 560mm/~22 inches (purple) fell over open waters.
(Photo Credit: Image : NASA/SSAI, Hal Pierce)
On Oct. 24 at 5 a.m. EDT/0900 UTC, Tropical Storm Raymond had maximum sustained winds near 45 mph/75 kph. Raymond is expected to strengthen a little over the next couple of days. Its center was located near latitude 14.7 north and longitude 105.3 west, about 305 miles/490 km south-southwest of Manzanillo, Mexico. Raymond is moving toward the west near 8 mph/13 kph and is expected to continue during the next couple of days. The estimated minimum central pressure is 1003 millibars.
The National Hurricane Center is forecasting Raymond to continue moving away from Mexico on a westward track.
Source: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center