On Feb. 9, 2013 at 2:30 a.m. EST, the sun erupted with an Earth-directed coronal mass ejection or CME, associated with a long duration C2.4-class flare. Experimental NASA research models, based on observations from the Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory (STEREO) and ESA/NASA's Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, show that the CME left the sun at speeds of around 500 miles per second, which is a fairly typical speed for CMEs. Historically, CMEs at this speed are usually benign.
Not to be confused with a solar flare, a CME is a solar phenomenon that can send solar particles into space and reach Earth one to three days later.
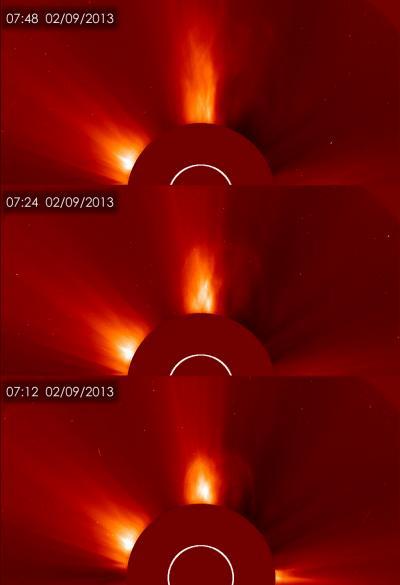
These images present three views over time of the coronal mass ejection (CME) released by the sun on Feb. 9, 2013 as seen by the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO).
(Photo Credit: : ESA&NASA/SOHO)
Earth-directed CMEs can cause a space weather phenomenon called a geomagnetic storm, which occurs when they connect with the outside of the Earth's magnetic envelope, the magnetosphere, for an extended period of time. In the past, CMEs at this strength have had little effect. They may cause auroras near the poles but are unlikely to disrupt electrical systems on Earth or interfere with GPS or satellite-based communications systems.
Source: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center