People suffering from swallowing difficulties, especially stroke patients, could be evaluated more efficiently and non-invasively thanks to research on a small sensor that's externally placed on the neck near the thyroid and records how a person swallows.
Ervin Sejdic, assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering in the University of Pittburgh's Swanson School of Engineering and primary author of a study on the sensor published online in IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, used simulation modeling to posit a mathematical solution to the low diagnostic success rate of current swallowing tests.
"We've seen a lot of patients, especially those suffering from strokes, die from difficulty swallowing," said Sejdic. "This disorder, known medically as dysphagia, can have dire consequences like malnutrition, dehydration, pneumonia, and even death. Unfortunately, current methods are often cumbersome and not as effective as they need to be."
In their paper,the authors suggest a mathematical algorithm that works electronically "behind the scenes" to improve the images captured by his neck sensor, which is the size of a quarter and affixed using double-sided tape. He and his team tested the model sensor on 40 dysphagic patients, who were instructed to take several sips of liquid in a head-neutral position. The result was a 90 percent success rate in diagnosing dysphagia.
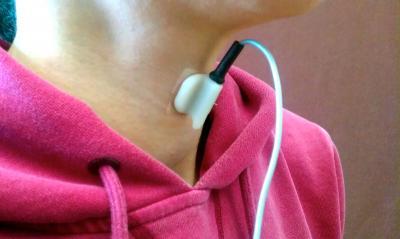
Researchers at University of Pittsburgh and the University of Toronto are developing a small sensor that's externally placed on the neck near the thyroid, which will record how a person swallows. The research team tested the model on 40 patients with swallowing difficulties, which resulted in a 90 percent diagnosis success rate, as opposed to the previous 50 percent rate. Photo Credit: N/A
Today's dysphagia evaluations make use of videofluoroscopy exams—motion x-rays prescribed by speech-language pathologists—that take snapshots of the throat, said Sejdic. These exams are effective at tracking whether food is going into one's airway instead of the stomach (aspiration); which parts of the mouth and throat may not be working well; and whether certain positions or strategies help a person swallow better.
"Unfortunately, people eat or drink something 10 to 20 times a day," said Sejdic. "And you can't put a person in front of an x-ray that many times, nor does every hospital have the capability to do so."
For stroke patients rushed into the hospital, an even more basic exam is administered. This includes simple water tests in which patients drink a glass of water and are evaluated on whether they cough or have "wet voice" (a condition where it sounds like patients are producing words through moisture). However, those tests show an even lower level of efficacy.
"These simple tests have a success rate below 50 percent," said Sejdic. "You're better off flipping a coin."
Sejdic and his colleagues have been working on their model sensor for almost three years, and negotiations are under way for a clinical trial in the United States and Canada. While the researchers' neck sensor could help all patients with dysphagia, they are specifically targeting stroke sufferers, as this occurs in 37 to 78 percent of those patients.
From the abstract:
The proposed algorithm is based on the wavelet packet decomposition of swallowing accelerometry signals in combination with linear discriminant analysis as a feature reduction method and Bayes classification. The proposed algorithm was tested using swallowing accelerometry signals collected from 40 patients during the regularly scheduled videoflouroscopy exam. The participants were instructed to swallow several five milliliter sips of thin liquid barium in a head neutral position. The results of our numerical analysis showed that the proposed algorithm can differentiate healthy swallows from aspiration swallows with an accuracy greater than 90%. These results position swallowing accelerometry as a valid approach for the detection of swallowing difficulties, particularly penetrationaspiration in patients suspected of dysphagia.
Citation: Sejdic, E., Steepe, C., Chau, T., 'Classification of penetration-aspiration versus healthy swallows using dual-axis swallowing accelerometry signals in dysphagic subjects', IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, Volume: PP, Issue: 99, DOI:10.1109/TBME.2013.2243730