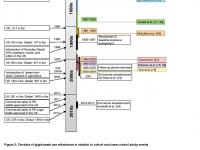
Exposure to glyphosate — the world’s most widely used, broad-spectrum herbicide and the primary ingredient in the weedkiller Roundup — increases the risk of some cancers by more than 40 percent, according to new research from the University of Washington.
Various reviews and international assessments have come to different conclusions about whether glyphosate leads to cancer in humans.