Successful technologies weave themselves into the fabric of society and essentially slip from our consciousness as have embedded control systems. Such systems with embedded computing units interact with some aspects of the physical world, are called hybrid systems.
Chinese Train Control System Level 3 (CTCS-3) with stringent reliability, safety, and performance requirements is the core element of the railway operations management system. Significant increase in train traffic require modern infrastructure strategies to accommodate high levels of traffic having standardized specification of the control system architecture and its behavior. The behavior of CTCS-3 is described by 14 basic operation scenarios consisting of different architectural components and communication among these components.
CTCS-3 is a hybrid system because it controls some aspect of the physical world: the movement of train. In a typical hybrid system, the control system, consisting of sensors, actuators, and computing units, interacts with its physical environment at discrete events. The behavior of a hybrid system is determined by composition the continuous evolution of physical environment, with discrete events of the control system.
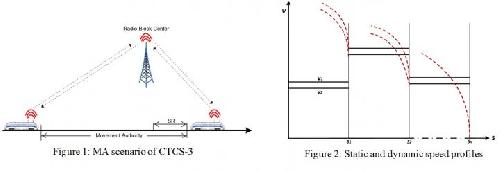 Figure 1 is an MA scenario of CTCS-3. Figure 2 shows static and dynamic speed profiles. Credit: ©Science China Press
Figure 1 is an MA scenario of CTCS-3. Figure 2 shows static and dynamic speed profiles. Credit: ©Science China Press
Combining continuous evolutions with discrete events to meet behavioral imperatives and constraints pose a great challenge to correct hybrid system modeling and verification. For CTCS-3, extensive interaction between computing units (Radio Block Center (RBC), Vital Computer, Driver Machine Interface, etc.), and the dynamics of train present this challenge.
As shown in Figure 1, in the CTCS-3, the train applies for movement authorization (MA) from the RBC and if granted, it gets permission to move within the track of the MA. A MA is composed of a sequence of segments where each segment has two speed limits (v1 and v2), a segment distance, and an operation mode of the train. Speed limits v1 and v2 (where v1 >= v2) represent the constraints for the train to apply emergency and normal service brake, respectively. This forms a classical hybrid system with a control-feedback loop, where the Controller regulates velocity of the Train by adjusting acceleration or deceleration \ on the basis of current velocity and position of the train and the information exchanged with the RBC for MA extension. Once the acceleration has been regulated by the Controller, train continues moving according to the differential equations s'=v, v'=a, where s is the position of the train, while v and a denote its velocity and acceleration, respectively.
Due to its extensive support for modeling, the Architecture Analysis & Design Language (AADL) is SAE International standard (AS5506B). AADL enables architecture-centric, model-based design of embedded systems. AADL defines a core architectural language to capture embedded system structure which can be extended with user selected properties and annex sublanguages.
For detailed behavior modeling and verification of hybrid systems, AADL has been extended with the Behavior Language for Embedded Systems with Software (BLESS) and Hybrid Annex (HA) sublanguages. BLESS uses a state transition system with guards and actions to model the discrete behavior of a control system. HA uses process algebra notations to model the continuous behavior of the physical environment its interaction with the control system. Both of these annexes support behavior specification with first-order predicates, augmented with simple temporal operators.
The structure of the CTCS-3 is modeled using the core AADL constructs. The discrete behavior of the control system is specified, modeled, and verified using BLESS. The verification that behavior meets specification produced a formal proof having 307 theorems. The continuous behavior of the train and the cyber-physical interaction (communication between the train and the controller) is modeled using the Hybrid annex and the system level behavior is verified using the Hybrid Hoare Logic (HHL) Prover theory of Isabelle/HOL.
This study firstly show how safety-critical hybrid systems can be modeled and verified in an integrated development environment which consists of AADL extended by the BLESS and HA annex sublanguages. AADL supports system integration through component contract specification based on interfaces and interactions and through well-defined semantics for extensive formal analysis at different architecture levels. This not only supports requirement identification for both discrete and continuous variables, but also facilitates assessment of correct operation of the physical portion of a hybrid system through several dependability-related analysis, and the certification of system level behavior correctness. Secondly, this study characterizes detailed behavior modeling and certifies three important system level properties of the MA scenario of the CTCS-3. Keeping in view the essential hybrid system design elements, researchers identify all the operational constraints, realize the discrete behavior modeling of the control system along with the continuous behavior modeling of its physical environment with the cyber-physical interaction, and verify the operational safety properties of trains under the MA scenario. The cyber-physical interaction, a major design challenge for hybrid systems, is modeled as communication events performed along data ports specified in type classifiers of AADL components. These communication events realize communication interrupts to preempt continuous evolution of controlled variables, modeling the physical dynamics of a train, according to the newly devised control strategy by the control system.
source: Science China Press